
According to the system, every transaction has two effects, a debit and a credit that are equal and opposite in nature. Accounting Equation is based on the double-entry bookkeeping system, which means that all assets should be equal to all liabilities in the book of accounts. All the entries made to the debit side of a balance sheet should have a corresponding credit entry on the balance sheet. When the total assets of a business increase, then its total liabilities or owner’s equity also increase. The equation is generally written with liabilities appearing before owner’s equity because creditors usually have to be repaid before investors in a bankruptcy.
Assets in Accounting: A Beginners’ Guide
This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends. It can be defined as the total number of dollars that a company would have left if it liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities. The major and often largest value assets of most companies are that company’s machinery, buildings, and property.
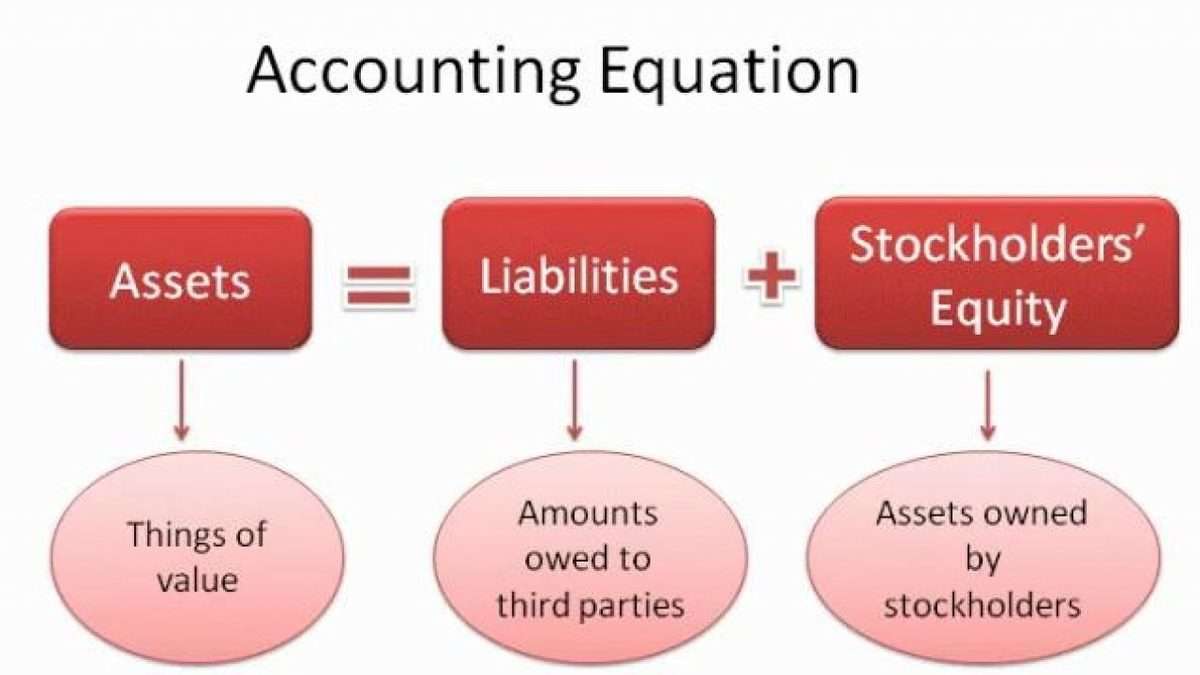
Assets Always Equal Liabilities Plus Equity
- As its name implies, the Accounting Equation is the equation that explains the relationship of accounting transactions.
- Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed.
- The equation is an important concept used to assess the financial condition of the company.
- Thus, all of the company’s assets stem from either creditors or investors i.e. liabilities and equity.
- The accounting engineering records the new asset and the use of cash.
- As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change.
For example, if the total liabilities of a business are $50K and the owner’s equity is $30K, then the total assets must equal $80K ($50K + $30K). The accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. This shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing. For example, when a company is started, its assets are first purchased with either cash the company received from loans or cash the company received from investors. Thus, all of the company’s assets stem from either creditors or investors i.e. liabilities and equity.
Accounting Equation Formula and Calculation
They include items such as land, buildings, equipment, and accounts receivable. It includes the amount that is owed by the shareholders, as a return on their investment in the company. Shareholder’s equity includes the amount that is invested by the shareholders in the form of shares, in addition to the retained earnings that have been accumulated by the company over the course of time.
The only equity is Sam’s capital (i.e., owner’s equity amounting to $100,000). Therefore cash (asset) will reduce by $60 to pay the interest (expense) of $60. Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. Understanding how the accounting equation works is one of the most important accounting skills for beginners because everything we do in accounting is somehow connected to it.
Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. Equity refers to the owner’s interest in the business or their claims on assets after all liabilities are subtracted.
The cumulative impact of all the additions and subtractions gives the ending amount which appears in the balance sheet at the end of the period. Therefore, the accounting equation is basically presented in the Balance Sheet such that the total holds. If hypothetically, the total does not hold, this means that some of the transactions (or class of accounts) have been categorized improperly. The accounting equation helps accountants to subsequently subcategorize the respective transactions into the double-entry system of accounting so that record-keeping and bookkeeping are done in a proper manner. It can be regarded as the very basis of maintaining accounts for any particular organization.
In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity. This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts. The accounting equation is not always accurate if it is unbalanced. This can lead to inaccurate reporting of financial statements and incorrect decisions made by management regarding money and investment opportunities. Let us imagine a business is set up and enters into a series of transactions over the first period.
Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 mortgage. This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage. The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. This refers to the owner’s interest in the business or their claims on assets after all liabilities are subtracted.
Debt is a liability, whether it is a long-term loan or a bill that is due to be paid. This arrangement can be ideal for sole proprietorships (usually unincorporated businesses owned by one person) in which the accounting equation is defined as: there is no legal distinction between the owner and the business. For example, John Smith may own a landscaping company called John Smith’s Landscaping, where he performs most — if not all — the jobs.

